Differences Between NTSC and PAL: Select the Better One for TV
Within the domain of television broadcasting, two prominent standards, NTSC and PAL, have exerted influence for an extended period. Although these acronyms may appear as technical terminology to some, they essentially embody the fundamental systems that regulate the display of images and the transmission of audio on our TV screens. This article will dig more differences between NTSC and PAL, so that you can find the better one to play the DVDs on your TV.

- GUIDE LIST
- Part 1. What is NTSC and PAL
- Part 2. Differences Between NTSC vs PAL
- Part 3. Can You Convert Between NTSC vs PAL
- Part 4. FAQs of NTSC vs PAL
Part 1. What is NTSC and PAL
NTSC, an abbreviation for the National Television System Committee, stands as a television broadcasting standard that originated in the United States. Introduced in the early 1950s, NTSC has gained widespread adoption in North America, Japan, and certain regions of South America. NTSC features a frame rate of 30 frames per second (fps) and a resolution of 525 lines.
PAL, which stands for Phase Alternating Line, is a television broadcasting standard developed in Germany. Predominantly used in Europe, Australia, and some parts of Asia, PAL operates at a frame rate of 25 fps and boasts a resolution of 625 lines.
Part 2. Differences Between NTSC vs PAL
There are a number of significant distinctions between the television transmission standards used by PAL (Phase Alternating Line) and NTSC (National Television System Committee). The following are the primary differences between PAL and NTSC:
| Feature | NTSC | PAL |
|---|---|---|
| Frame Rate | 30 frames per second (fps) | 25 fps |
| Lines per Frame | 525 lines | 625 lines |
| Color Subcarrier Frequency | 3.58 MHz | 4.43 MHz |
| Color Encoding | NTSC uses YIQ color space | PAL uses YUV color space |
| Color Reproduction | NTSC can have color accuracy issues, known for ‘NTSC color’ or ‘Never Twice the Same Color.’ | PAL generally offers more accurate and consistent color reproduction. |
| Field Rate | 60 fields per second (interlaced) | 50 fields per second (interlaced) |
| Resolution | NTSC has a resolution of 720×480 pixels | PAL has a resolution of 720×576 pixels |
| Geographical Use | Common in North America, Japan, parts of South America and Asia. | Common in Europe, Australia, Africa, parts of Asia, and the Middle East. |
| Compatibility | NTSC devices may not be compatible with PAL devices, and vice versa. | PAL devices may not be compatible with NTSC devices, and vice versa. |
| Artifacting Issues | More prone to flicker and dot crawl due to its lower frame rate. | Less prone to flicker and dot crawl due to its higher frame rate. |
| Audio Carrier Frequency | 4.5 MHz (BTSC) in the U.S. | 5.5 MHz in most PAL regions |
| Broadcast Standards | NTSC-M (USA, Canada, Mexico) | PAL-B/G (Europe, Australia), PAL-I (UK, Ireland), PAL-D/K (most of Eastern Europe) |
NTSC VS PAL: Color & Picture Quality
The color encoding is one obvious distinction. PAL uses 4.43 MHz for color subcarrier frequency, whereas NTSC uses 3.58 MHz. As a result, there are differences in how colors are represented; PAL is frequently seen to offer somewhat superior color quality.
NTSC: It is renowned for its problems with color accuracy. It employs the YIQ color space, thus color reproduction variances are frequently apparent. Funny names for this include “NTSC color” and “Never Twice the Same Color.” Dot crawl and flicker are two other obvious abnormalities that NTSC may display, particularly in scenes with rapid motion. Perceived motion problems may be exacerbated by the reduced frame rate (30 frames per second).
PAL: When compared to NTSC, PAL often provides more precise and reliable color reproduction. Better color fidelity is a result of PAL's usage of the YUV color space. Due to its greater frame rate (25 fps) and other technical differences, PAL typically has a better picture quality with less flicker and dot crawl. Better vertical resolution is also facilitated by the increased number of lines. Also, you can change video resolution to get a better quality.
NTSC VS PAL: Audio Quality
Stereo audio is supported by both NTSC and PAL, however the sound carrier frequency is different. PAL employs 5.5 MHz, while NTSC utilizes 4.5 MHz. The ordinary spectator might not detect the slight difference.
NTSC: In general, NTSC audio quality is good. In the US, 4.5 MHz (BTSC) is usually the audio carrier frequency for NTSC.
PAL: PAL offers high-quality audio as well, and in the majority of PAL regions, the standard audio carrier frequency is 5.5 MHz.
You can change audio of a video file when you want to get a superb audio quality.
NTSC VS PAL: Bandwidth
A larger bandwidth is needed for PAL than for NTSC due to its higher frame rate and resolution. This implies that the number of channels that can be broadcast simultaneously may be impacted by the requirement for PAL transmissions to have more data transfer capacity.
NTSC: Compared to PAL, NTSC requires less bandwidth because to its lower frame rate (30 fps) and lower vertical resolution (525 lines).
PAL: PAL requires a somewhat larger bandwidth than NTSC because to its greater frame rate (25 fps) and vertical resolution (625 lines).
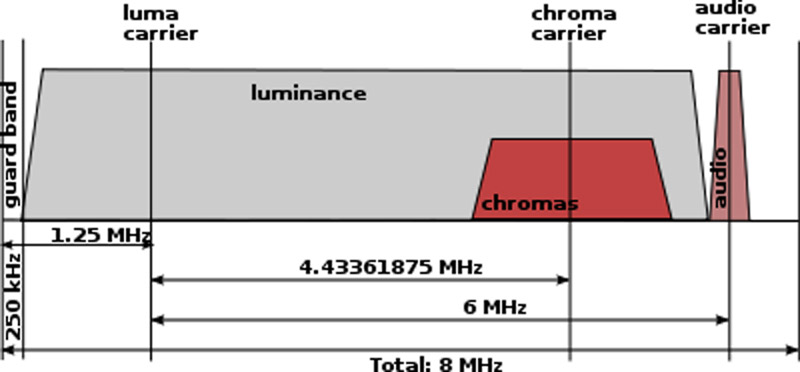
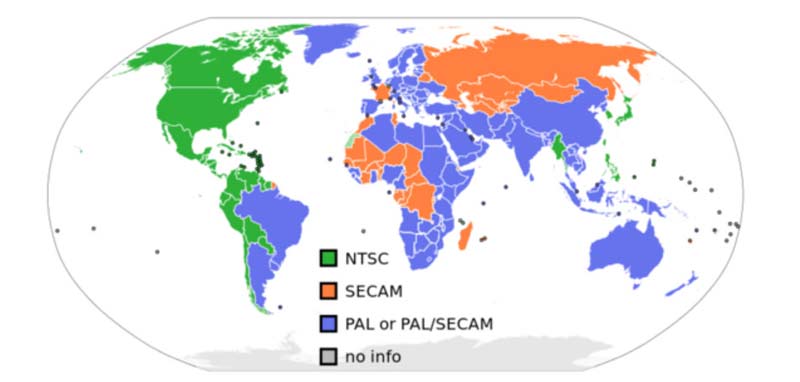
NTSC VS PAL: Geographic Distribution
Geographical considerations play a major role in the decision between NTSC and PAL, with nations choosing the standard that best suits their broadcast infrastructure.
NTSC: Widely used in North America, Asia, Japan, and portions of South America. The particular version that is utilized in the US, Canada, and Mexico is called NTSC-M.
PAL: Widely used throughout the Middle East, Europe, Australia, and parts of Africa and Asia. PAL-B/G (Europe, Australia), PAL-I (UK, Ireland), and PAL-D/K (much of Eastern Europe) are examples of specific variations.
Compatibility and smooth performance depend on your understanding of these distinctions, especially when using older analog video equipment. These historical discrepancies are less difficult to overcome thanks to the built-in converting capabilities of modern digital equipment.
Part 3. Can You Convert Between NTSC vs PAL
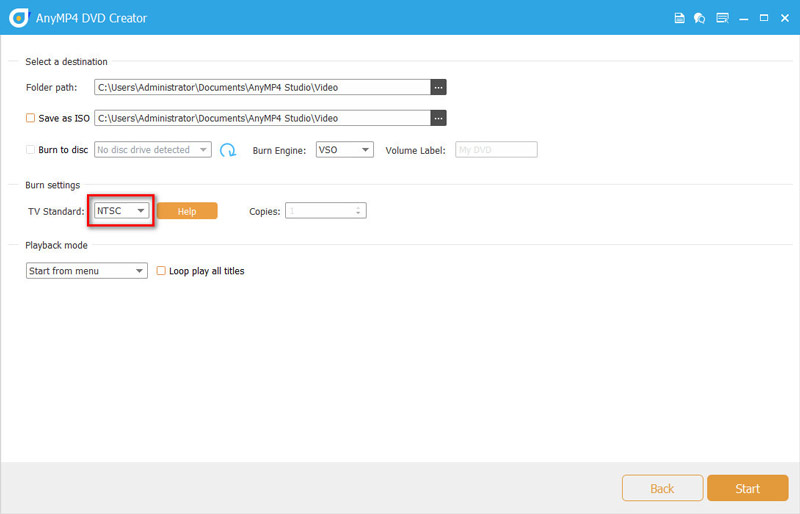
Yes, it is possible to convert between NTSC and PAL formats using tools like AnyMP4 DVD Creator. This software facilitates seamless conversion between NTSC and PAL when burning a DVD, allowing users to enjoy content across different standards without losing quality.
It is also easy to convert NTSC to PAL and PAL to NTSC with this DVD burner.
Run this DVD burner on your Windows or Mac computer.
Select DVD Disc. Then import the videos that you want to make in a DVD.
Edit the DVD menu, and edit the DVD movie.
In the export option, select NTSC or PAL next to Burn Engine as you like.
Click Start to output the DVD files in NTSC or PAL format.
For more NTSC to PAL converters, you can find them here.
Part 4. FAQs of NTSC vs PAL
Does PAL and NTSC matter anymore?
Because digital formats are so widely used in the modern era, the difference between NTSC and PAL is less significant. Compatibility problems, however, could still occur occasionally.
Is US PAL or NTSC?
The United States primarily uses the NTSC standard for television broadcasts. PAL, on the other hand, is a television broadcast standard used in other regions, such as Europe, Asia, Africa, and parts of South America.
Is Singapore PAL or NTSC?
Singapore uses the PAL (Phase Alternating Line) television broadcast standard.
Why is NTSC better than PAL?
Because digital formats are so widely used in the modern era, the difference between NTSC and PAL is less significant. Compatibility problems, however, could still occur occasionally.
How much slower is PAL than NTSC?
Because digital formats are so widely used in the modern era, the difference between NTSC and PAL is less significant. Compatibility problems, however, could still occur occasionally.
Conclusion
NTSC and PAL coexist in the changing television standards landscape, influencing our perception of both visual and audio material. Recognizing their distinctions helps broadcasters and audiences alike negotiate the challenges of international media consumption. Even if the effects of these standards are becoming less significant due to technological developments, they nevertheless influence how we watch and serve as a reminder of the early days of television technology.
What do you think of this post? Click to rate this post.
Excellent
Rating: 4.9 / 5 (based on 643 votes)
Find More Solutions
ArkThinker Free MKV to MP4 Converter Online [Fast and Safe] 10 GIF Converters to Convert Between Images/Videos and GIFs Effortless MOV to MP4 Conversion: Step-by-Step Process 7 Best VCR/VHS DVD Recorders and DVD Recording Software Effortless MOV to MP4 Conversion: Step-by-Step Process 5 Best Video Resolution Converters for Different PlatformsRelative Articles
- Edit Video
- How to Make a Short Video Longer with 3 Different Methods
- Loop a Video on iPhone, iPad, Android Phone, and Computer
- Free Video Editing Software – 7 Best Free Video Editor Apps
- 3 TikTok Watermark Remover Apps to Remove TikTok Watermark
- Video Filter – How to Add and Put a Filter on a Video 2024
- How to Slow Down a Video and Make Slow Motion Video 2024
- Split Your Large Video File with 3 Best Movie Trimmers 2024
- How to Add Watermark to Video on Different Devices 2024
- 5 Best MP4 Compressors to Reduce the Video File Size 2024
- Detailed Guide on How to Slow Down a Video on Snapchat 2024



